Welcome to the future of mental health care! In a world where traditional therapies sometimes fall short, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is emerging as a groundbreaking alternative for those battling depression and anxiety. But what exactly does “TMS Treatment APN” entail? Whether you’re seeking insight for yourself or someone you love, our quick guide will demystify this innovative treatment option. Join us as we explore the ins and outs of TMS therapy, from its science-backed benefits to what you can expect during your journey towards relief. Ready to take the first step towards reclaiming joy in your life? Let’s dive in!
Introduction
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) treatment has emerged as a groundbreaking option for individuals struggling with mental health conditions, particularly depression. As traditional therapies sometimes fall short, TMS offers a non-invasive solution that stimulates specific areas of the brain. But who administers this innovative treatment? Enter Advanced Practice Nurses (APNs). These skilled professionals bring their expertise and compassionate care to the forefront of TMS therapy, enhancing outcomes for patients in profound ways. Let’s explore how APNs are transforming the landscape of mental healthcare through TMS treatment and what it means for those seeking relief from their symptoms.
Definition and process of TMS treatment
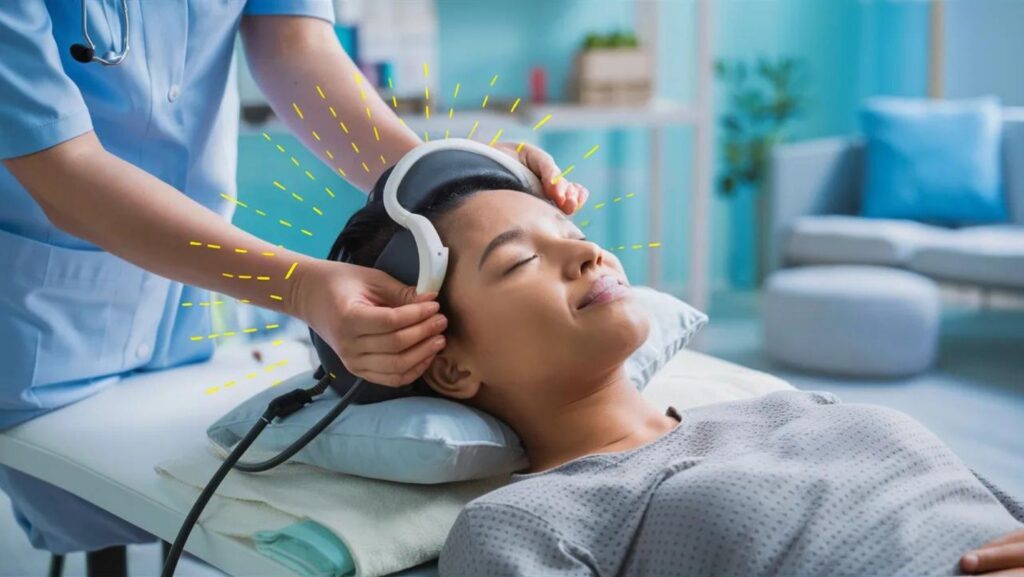
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive treatment for depression and other mental health disorders. It utilizes magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain.
During a TMS session, an electromagnet is placed against the scalp. This device generates pulses that target specific areas linked to mood regulation.
The process typically lasts about 30-40 minutes per session. Patients often undergo multiple sessions over several weeks. Many find it easy to fit into their daily routines since there’s no need for anesthesia or recovery time.
Patients may feel a tapping sensation on their head during treatment, which is generally well-tolerated. Over time, these targeted magnetic pulses can enhance neural connectivity and improve overall brain function related to mood stability.
With its growing popularity, TMS offers hope for individuals seeking alternative therapies when traditional medications have not yielded desired results.
The role of APNs in administering TMS treatment
Advanced Practice Nurses (APNs) play a crucial role in the administration of TMS treatment. They are equipped with specialized training that allows them to understand both the technical and emotional aspects of this therapy.
During sessions, APNs monitor patients closely for any side effects or discomfort. Their expertise ensures that each patient’s experience is tailored to their unique needs, fostering a supportive environment.
They also educate patients about what to expect from TMS treatment. This guidance helps alleviate anxiety and promotes adherence to the therapeutic process.
Moreover, APNs collaborate with psychiatrists and mental health professionals, ensuring an integrated approach to patient care. Their involvement bridges gaps in communication and enhances overall treatment outcomes.
With their holistic perspective on healthcare, APNs effectively assess not just symptoms but also psychosocial factors influencing recovery.
Advantages of having APNs involved in TMS treatment
The involvement of Advanced Practice Nurses (APNs) in TMS treatment brings a wealth of benefits to mental healthcare. Their extensive training equips them with the skills necessary to effectively assess and monitor patients throughout the process.
APNs can provide personalized care plans tailored to individual needs. This approach enhances patient engagement and promotes better outcomes, as they take time to understand each patient’s unique circumstances.
Additionally, APNs offer a holistic perspective that integrates physical health into mental health treatments. They can address coexisting medical conditions that may impact therapy effectiveness.
Their presence also fosters strong therapeutic relationships. Patients often feel more comfortable discussing their concerns with APNs, which can lead to improved adherence to treatment protocols.
Lastly, having APNs involved helps alleviate some responsibilities from psychiatrists and other specialists, enabling a more streamlined workflow in busy clinical settings. This collaboration ultimately contributes to enhanced patient care overall.
How TMS treatment by APN can improve patient care
TMS treatment administered by Advanced Practice Nurses (APNs) introduces a personalized touch to mental health care. APNs are trained to assess individual patient needs effectively, ensuring that each TMS session aligns with specific therapeutic goals.
Their expertise extends beyond just administering the treatment. APNs can monitor patients’ responses in real-time, adjusting protocols as necessary for optimal results. This adaptability often leads to quicker improvements in symptoms.
Furthermore, the holistic approach of APNs fosters stronger relationships with patients. Open communication helps build trust and encourages adherence to treatment plans. Patients feel valued and understood, which is crucial for successful outcomes in mental healthcare.
With their comprehensive skill set, APNs enhance not only the quality but also the accessibility of TMS therapy. Their involvement bridges gaps between complex psychiatric care and patient-centered practices, creating a more supportive environment for recovery.
Success stories and case studies of TMS treatment by APN
Many patients have shared their transformative experiences with TMS treatment administered by Advanced Practice Nurses (APNs). One notable case involved a young woman battling severe depression. After several sessions, she reported significant improvements in her mood and overall quality of life.
Another success story features a veteran suffering from PTSD. With the guidance of an APN, he underwent TMS therapy and found relief from symptoms that had plagued him for years. His journey inspired others in similar situations to seek help.
In both instances, the involvement of APNs ensured personalized care tailored to each patient’s unique needs. Their expertise not only facilitated effective treatment but also fostered a supportive environment where patients felt heard and understood.
These case studies illustrate how skilled APNs can make a meaningful difference in delivering TMS therapy, enhancing patient outcomes while promoting mental wellness in various populations.
Potential drawbacks or challenges of using TMS treatment by APN
While TMS treatment by APNs presents numerous benefits, there are some potential drawbacks to consider.
One challenge is the limited availability of trained APNs. Not every facility has access to professionals skilled in administering TMS therapy, which can affect patient wait times and overall accessibility.
Another concern involves varying levels of experience among APNs. Different backgrounds may lead to inconsistent application of techniques and protocols that could impact treatment efficacy.
Additionally, insurance coverage for TMS therapy varies widely. Some patients might face financial barriers if their plans do not recognize treatments administered by APNs as valid.
Finally, there’s a risk that patients may feel less comfortable receiving care from an advanced practice nurse instead of a psychiatrist or psychologist. This perception can influence engagement and trust in the therapeutic process.
Comparing TMS treatment by APN to other forms of therapy for mental health conditions
TMS treatment by APNs offers a distinct approach compared to traditional therapies like talk therapy or cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). While these methods rely heavily on verbal communication and the therapeutic relationship, TMS focuses on stimulating specific brain regions without direct conversation.
Moreover, TMS is a non-invasive procedure that can provide relief for patients who may not respond well to medications. This sets it apart from pharmacological treatments, which often come with side effects and require careful monitoring.
Patients seeking alternatives to conventional approaches might find TMS appealing due to its targeted nature. The addition of APNs in this process enhances care quality, as they bring their expertise in patient management and assessment.
For those struggling with severe depression or anxiety disorders, the choice between TMS by an APN and other therapies could lead to personalized outcomes that significantly improve mental health status.
Conclusion
The landscape of mental healthcare is evolving, and the role of Advanced Practice Nurses (APNs) in TMS treatment stands out as a promising development. As the demand for effective mental health solutions grows, APNs are positioned to bridge gaps in care delivery. Their extensive training allows them to not only administer TMS therapy but also provide comprehensive patient support throughout the process.
With their unique skill set, APNs can enhance patient education and ensure consistent follow-up care. This holistic approach may lead to better treatment adherence and improved outcomes for individuals struggling with conditions like depression or anxiety.
As more facilities embrace TMS treatment by APN, we could see significant shifts in how mental health services are delivered. The integration of APNs may pave the way for collaborative care models that prioritize accessibility and efficiency in treatment.
Ultimately, the future impact of APNs on TMS therapy could redefine standards within mental healthcare, making it more patient-centered while addressing critical gaps often seen in traditional settings. The potential here is immense and holds great promise for both practitioners and patients alike.